- Gurugram
- info@ravemultimedia.com
- +91 8130133699
Varun Singh
august 21,2023
How ONDC works on the partner’s end
This blog will discuss ONDC, how it works at the partner’s end, and the underlying pricing strategies.

The is a groundbreaking system bolstered by the Indian government. Its primary focus is to democratise the digital commerce landscape in India.
Furthermore, it will serve as an alternate solution to curb monopolistic tendencies and create a balanced marketplace. Beyond a mere platform, ONDC fosters direct links between shoppers, tech platforms, and 39,000 active sellers across 273 cities. This initiative empowers consumers to explore diverse retailers and ensure the best prices while promoting inclusivity.
What is ONDC?
Core Principles
- Decentralisation: Moves away from traditional monolithic platforms.
- Interoperability: Facilitates transactions across diverse digital platforms.
- Openness: Encourages widespread integration and adoption
Technological Backbone
Harnesses advanced technologies, such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
Scope
Encompasses both B2C and B2B transactions, streamlining digital commerce across sectors.
How ONDC Operates?
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) boasts a technologically advanced architecture designed to revolutionise the digital commerce landscape in India. Let’s delve into its operational intricacies:
Technology Components
Adaptor Interfaces:
● Essentially the open APIs were developed in line with the open-source interoperable specification of the Beckn protocol.
●Purpose: To facilitate the seamless exchange of transaction-related information, enabling a standardised interaction across the network.
● Source of Documentation: Comprehensive documentation for these interfaces is available at www.ondc.org.
Gateway:
●A pivotal application facilitating the discoverability of all network sellers.
● How it Works: It multicasts search requests from buyer applications to seller applications, filtering based on criteria such as location and availability.
● Future Evolution: Although initially provided by ONDC’s tech partners, the vision encompasses multiple independent gateway providers with diverse service offerings.
Buyer and Seller Side Applications:
● Applications that enable transactions on the ONDC network.
● Initial Strategy: ONDC might introduce reference applications independently or via tech partners. These reference applications will also be open-source, encouraging service providers to integrate and evolve with the ONDC network.
Open Registries:
● These applications maintain crucial data, such as a list of ONDC participants and network policies.
Buyer-Side Apps:
●A pivotal application facilitating the discoverability of all network sellers.
● How it Works: It multicasts search requests from buyer applications to seller applications, filtering based on criteria such as location and availability.
● Future Evolution: Although initially provided by ONDC’s tech partners, the vision encompasses multiple independent gateway providers with diverse service offerings.
Seller-Side Apps:
● Symbolising the supply side of any transaction.
.
● Functions: Receive buyer requests, publish their catalogue of offerings, and execute buyer orders.
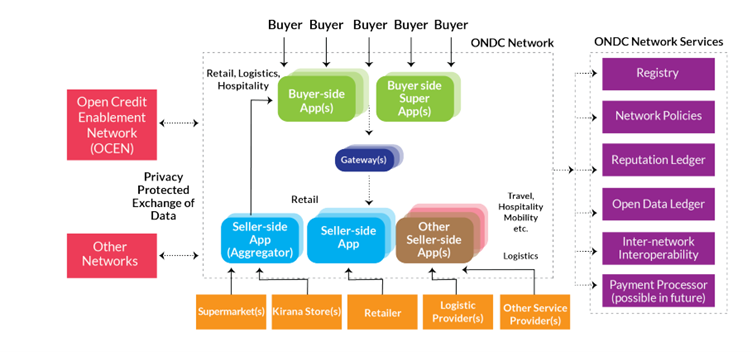
The ONDC’s operational model is a testament to its commitment to efficiency, scalability, and interoperability, ensuring that both buyers and sellers experience a seamless digital commerce journey.
Transaction Model of ONDC
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) has intricately structured its operations to ensure a trustworthy and streamlined transaction lifecycle. It harnesses a multi-levered approach, entwining operational measures with the stages of a transaction, ensuring every participant can trust the process. Let’s dissect the successive stages and understand the ONDC’s mechanisms to bolster trust:
- Search and Discovery: Here, buyers embark on their journey, scouring for desired products and subsequently receiving a roster of potential sellers.
- Order Placement: At this juncture, buyers finalise their selection, add items to the cart, and confirm their orders. Notably, ONDC’s framework interweaves the process of finalising delivery arrangements within this stage, distinguishing it from conventional platforms.
- Fulfilment: Beyond mere delivery execution, this stage incorporates the nuances of logistical arrangements, aligning them closely with the order placement phase.
- Payment and Settlement: Encompassing the financial dimensions, buyers conclude their payments whilst stakeholders receive their remunerations. Typically, payment ratifies the order, with settlements unfolding subsequently.
- Returns, Refunds, and Cancellations: Though not a conventional stage, its frequent occurrence necessitates a robust and systematic model to ensure efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Issue and Grievance Management: Operating as an exception-handling mechanism, this can manifest at any transactional stage, especially post-order confirmation and payment.
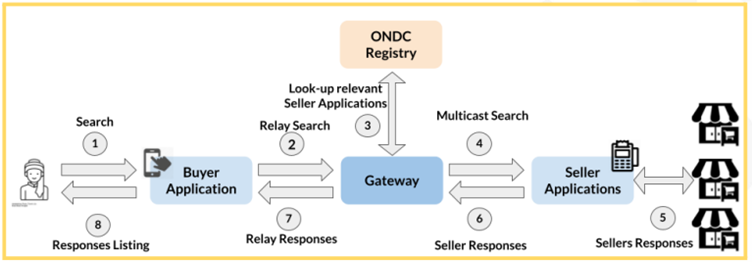
This lifecycle remains universally applicable regardless of the product or service domain, from retail groceries to travel. Additionally, ONDC has integrated trust-enhancing measures that transcend these stages, providing an overarching assurance layer.
Payment and Settlement in the ONDC Model
With the innovative unbundling approach of the e-commerce value chain in ONDC, payment and settlement responsibilities span multiple participating entities. This unique structure prioritises decentralisation over the traditional centralised payment systems seen in conventional e-commerce.
Overview of ONDC’s Payment Structure
- Central Platform Versus ONDC Model:
- Traditional E-Commerce: Sellers traditionally rely on a single, central platform for the assurance of payment collection and settlement.
- ONDC Model: The payment and settlement obligations are spread across various entities participating in the process.
Key Entities in the Payment Cycle
- Collector Network Participant (NP):
- Role: Can be either the Buyer App or the Seller App.
- In Cash on Delivery (CoD) scenarios: The NP responsible for logistics (either on-network or off-network) assumes the role of the Collector. The overarching process remains consistent.
- Recipient Network Participants:
- Definition: These are other NPs (the counterparty NP and the Logistics Service Provider) involved in the transaction.
The ONDC Settlement Flow
The Reconciliation Service Providers (RSP) and Settlement Agencies are the core of ONDC.Reconciliation Service Providers (RSP):
- Role: Ensure accurate and timely settlements between the Collector NP and the Recipient NPs.
- Process:
- Post-transaction completion (order confirmation and payment finalisation), the RSP retrieves settlement terms and amounts from the Transaction-level contract between relevant Network Participants.
- One of these participants is designated the Collector, while others are Receivers.
- Based on the received terms, the RSP creates a bit of settlement advice for the Collector’s designated Settlement Agency.
Settlement Agencies:
- Role: Execute the actual fund transfers based on the RSP’s settlement advice.
- Process:
- Upon receiving the settlement advice, the agency initiates payments to the Recipient NPs through their respective banks.
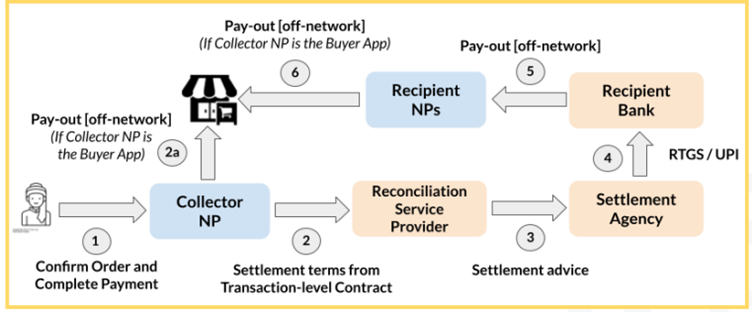
This methodological approach by ONDC ensures a seamless, efficient, and decentralised payment and settlement system, maintaining transparency and reliability across the e-commerce spectrum.
